Building Blocks
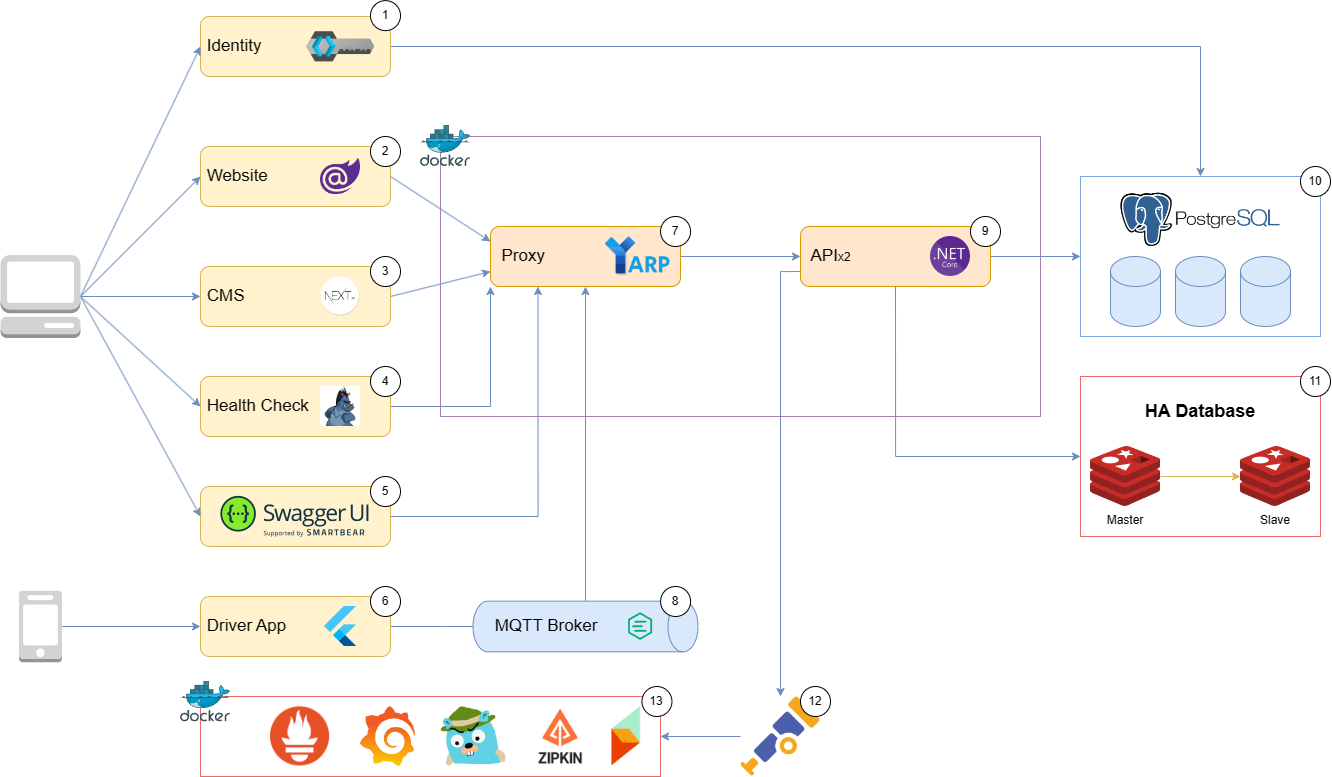
Components
CMS:
This component serves as a central hub for managing information related to transportation processes. It likely includes features such as order management, vehicle tracking, and driver information management. The CMS also provides a dashboard for managers to monitor and oversee the entire transportation process. This dashboard may display real-time data, analytics, and reports to help managers make informed decisions. Next.js is a web framework used to develop the CMS. It's a React-based framework that allows for the creation of dynamic web pages. It's also a popular choice for building server-side rendered applications.
Customer Website:
Customers can use this website to look up information about their orders, and there's also a feature to view the history of their previous orders. This website is built using Blazor Server, which is a web framework for building interactive web UIs using C# instead of JavaScript. It's a popular choice for building server-side rendered applications.
Load Balancer:
YARP, or Yet Another Reverse Proxy, serves as a load balancer. It distributes incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure efficient utilization and prevent overloading. The Load Balancer also provides a dashboard for managers to monitor the load on the servers. This allows them to optimize resource allocation.
Driver App:
The Driver App is a mobile application developed using the Flutter framework. It's intended for drivers to monitor the transportation process. One of its primary functions is to send the real-time location of vehicles to the central server, likely using GPS or other location services.
MQTT Broker:
EMQX serves as an MQTT broker, which is a messaging protocol often used for IoT and real-time data communication. In this context, it receives vehicle location data from the Driver App and forwards it to the server for further processing. We have integrated EMQX with the Redis database to store the location data for later retrieval.
Identity Server:
Keycloak is an identity and access management system used for user authentication and authorization. It manages user accounts for your application and provides Single Sign-On (SSO) capabilities, making it convenient for users to access various parts of the system without repeated logins.
API Server:
The API Server is the core of your system for handling data transmission. It receives vehicle location data from the MQTT Broker and interacts with the database. It also serves as the interface for clients (such as the Next.js customer website) to access information about orders, vehicles, drivers, and other transportation-related data.
Database:
- PostgreSQL is used as the primary database to store structured data related to orders, vehicles, drivers, and transportation processes. It's also used for storing user accounts and other information related to the Identity Server. Database Replication is used to improve performance and reliability by distributing data across multiple servers.
- Redis, on the other hand, is utilized for caching data, which can improve system performance by reducing the need to retrieve data from the database repeatedly. With High Availability, Redis can also be used as a backup database in case of a database failure.
OpenTelemetry Collector:
This component collects telemetry data from various parts of your system, including applications and services. It's responsible for forwarding this telemetry data to processing and monitoring tools for analysis, diagnostics, and performance optimization.
Health Check:
The Health Check component continuously monitors the health of your servers and services. It reports the health status to the Load Balancer, allowing it to make informed decisions about routing traffic to healthy servers.
Exporter:
These are various monitoring and analysis tools used to export and visualize telemetry data collected by the OpenTelemetry Collector. Grafana, Prometheus, Jaeger, Seq, and Zipkin are commonly used tools in the DevOps and observability space.
API Architecture & Patterns
Clean Architecture
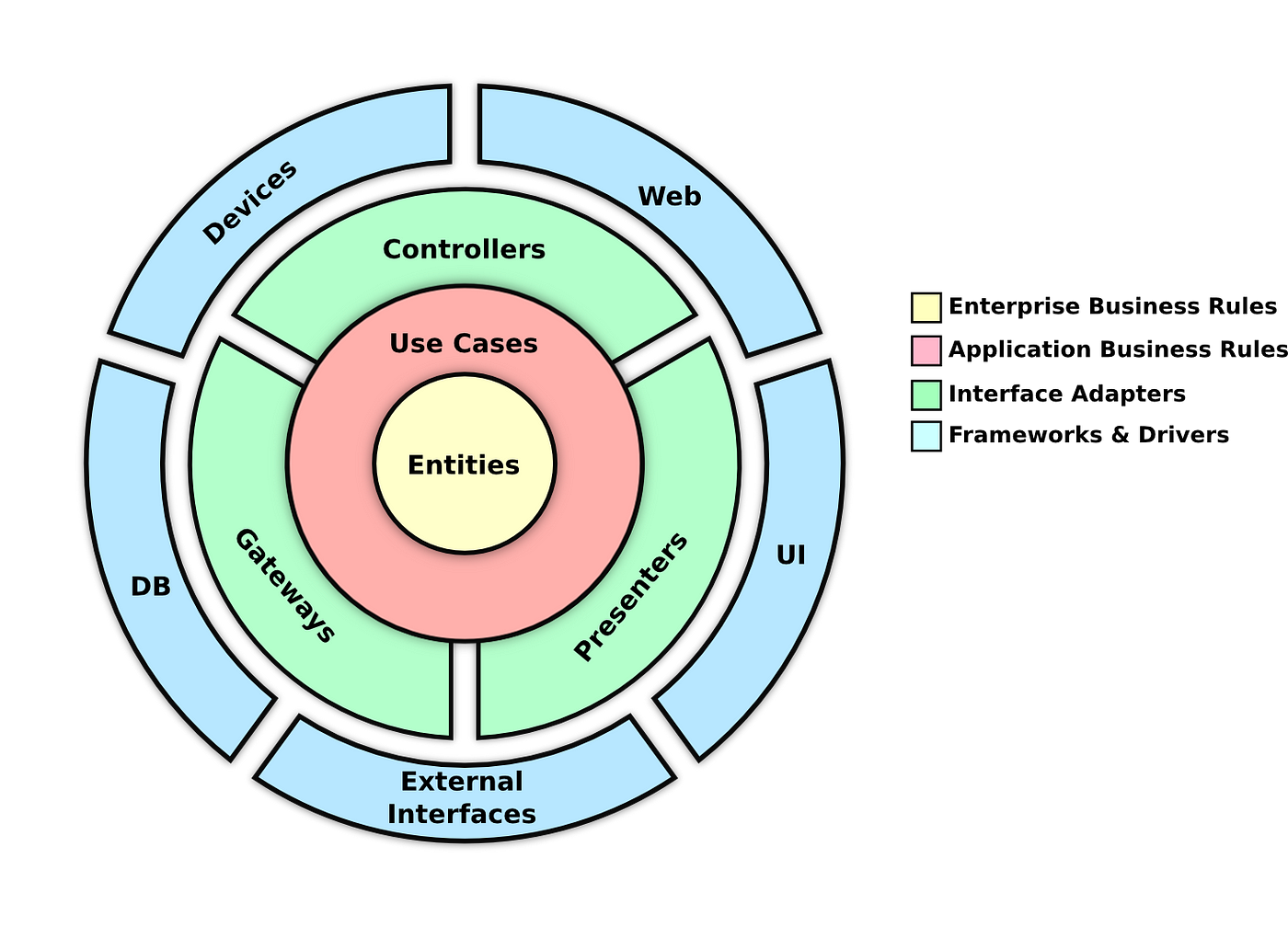
Clean Architecture is a software design principle that emphasizes organizing code in a way that separates concerns, making it easier to maintain and test. It divides an application into distinct layers: the Core (containing business logic and entities), Use Cases (defining application-specific rules), Interface Adapters (connecting to the outside world), and Frameworks/Drivers (external dependencies). This separation allows for flexibility, testability, and maintainability, reducing the risk of unintended side effects when making changes. Clean Architecture promotes robust and adaptable software systems.
Design Patterns
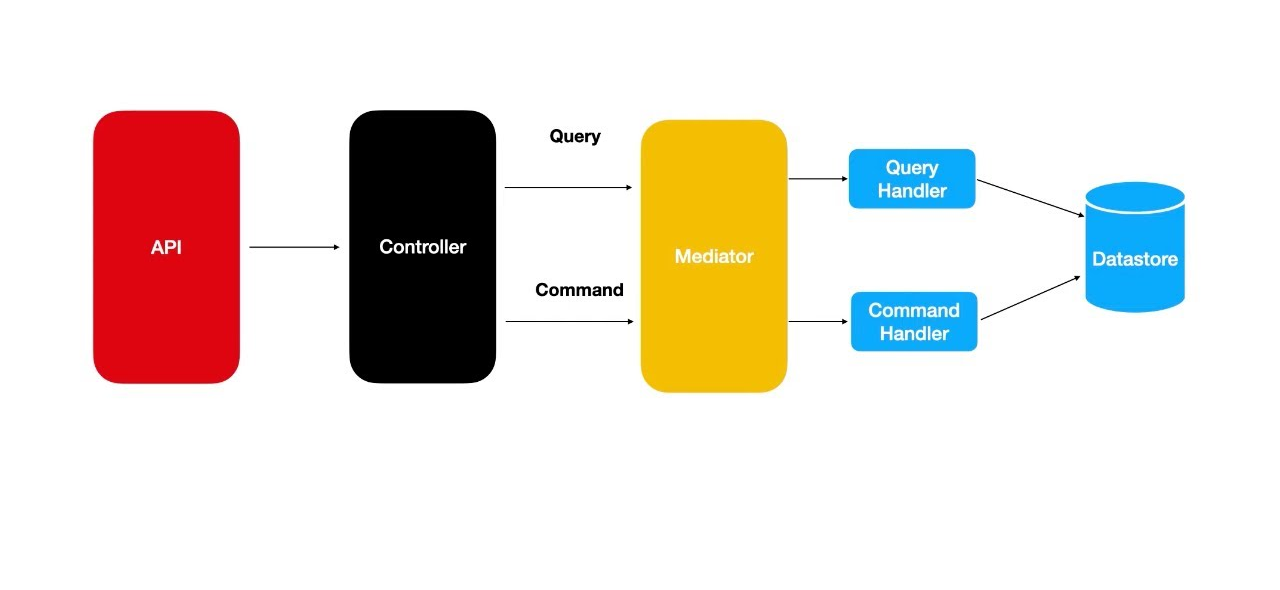
CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation) is a software design pattern that separates the read and write operations of a system into two distinct models. The Command model handles write operations, while the Query model handles read operations. This separation allows for the optimization of each model for its specific purpose, improving performance and scalability. The Mediator Pattern is used to implement CQRS, decoupling the Command and Query models and enabling communication between them. The Mediator Pattern also allows for the addition of new handlers without modifying existing handlers, improving the system's flexibility and maintainability.
We have also implemented the following design patterns:
- Repository Pattern
- Unit of Work
- Specification Pattern
- Options Pattern
- Inversion of Control / Dependency Injection
Communication Protocols
HTTP
Client-server communication is handled using the HTTP protocol. HTTP is a widely used application-layer protocol for transmitting data between clients and servers. It is a stateless protocol, meaning that each request is independent of the previous request. HTTP is a reliable and efficient protocol for client-server communication.
MQTT
The GPS tracking functionality is implemented using the MQTT protocol. MQTT is a lightweight messaging protocol designed for IoT devices. It is a publish-subscribe protocol, meaning that clients can subscribe to topics and receive messages published to those topics. MQTT is a reliable and efficient protocol for real-time communication.
OTLP
The OpenTelemetry Protocol (OTLP) is used for transmitting observability data. OTLP is a protocol for transmitting telemetry data, including traces, metrics, and logs. OTLP is a reliable and efficient protocol for transmitting observability data.